Follow Us On:
Generative AI: The Technology That’s Redefining Creation
In the past decade, the pace of technological innovation has been nothing short of breathtaking. From the rise of cloud computing to the expansion of edge devices, the way we create, consume, and distribute information has evolved dramatically. One of the most transformative advancements to emerge in recent years is generative AI. Unlike traditional AI systems that primarily analyze or classify data, AI can create — generating text, images, audio, and even code that appears convincingly human-made.
The concept might sound like science fiction, but it has already moved into everyday applications. Whether it’s chatbots holding meaningful conversations, tools that generate photorealistic images from simple prompts, or AI systems that compose music, AI has become a cornerstone of the digital transformation era. In this article, we’ll explore the inner workings, key applications, challenges, and ethical considerations of this groundbreaking technology.
To appreciate the potential of AI, it’s essential to understand what sets it apart from other AI forms. Traditional AI models excel at prediction and classification. For example, a conventional machine learning algorithm might predict whether an email is spam or not based on its features. In contrast, AI goes a step further — it can generate entirely new content that aligns with the patterns it has learned from existing data.
At its core, AI uses machine learning architectures like Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) and Transformer-based models. These systems learn from massive datasets and are able to mimic the distribution of data they are trained on.
While AI research has been ongoing since the mid-20th century, the practical rise of AI began around the 2010s, spurred by increases in computational power and the availability of big data. Breakthroughs like the 2014 introduction of GANs by Ian Goodfellow and the 2017 Transformer paper by Vaswani et al. laid the foundation for the current boom.
Key milestones include:
These developments have expanded AI beyond research labs and into industries ranging from healthcare to entertainment.
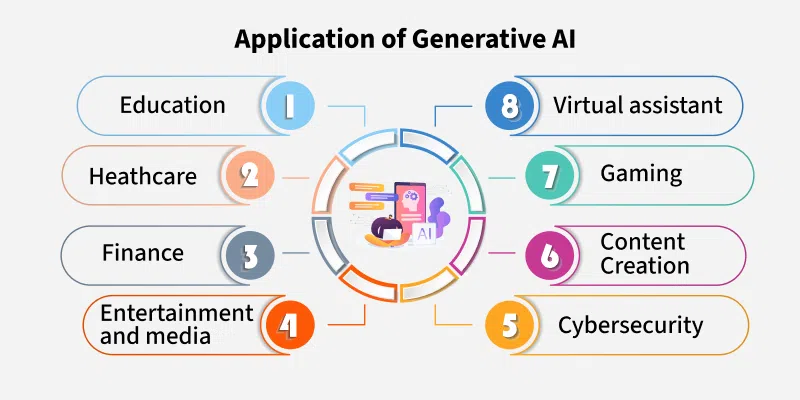
The beauty of AI lies in its versatility. It can be applied in virtually every sector, often transforming how businesses operate.
Writers, marketers, and journalists are increasingly turning to AI for drafting articles, producing ad copy, and even creating scripts. These tools can speed up content production while maintaining quality.
Artists and designers leverage AI to produce realistic visuals or conceptual artwork. Film studios can use it for pre-visualization or special effects, saving both time and resources.
In the medical field, AI assists in drug discovery, creating models of protein structures or simulating molecular interactions far faster than traditional methods.
Game developers employ AI to create immersive environments, generate NPC dialogues, and even produce unique quests, leading to more dynamic player experiences.
Adaptive learning platforms powered by AI can create customized lesson plans, quizzes, and feedback tailored to each student’s needs.
The effectiveness of AI is rooted in complex algorithms and large-scale training.
Deep neural networks form the backbone of most AI systems, allowing them to identify intricate patterns within datasets.
High-quality input data is critical. Before training, data is cleaned, normalized, and often augmented to improve the model’s performance.
Training a AI model involves feeding it vast amounts of data, adjusting parameters through backpropagation, and fine-tuning it for specific use cases.
While powerful, AI isn’t without challenges.
Because generative AI learns from existing data, it can inherit and amplify biases present in that data.
The same tools that can create beautiful art can also generate convincing deepfakes or misleading text.
Training large-scale generative AI models demands significant resources, both financially and environmentally.
The capabilities of generative AI raise pressing ethical questions.
Balancing innovation with responsibility is one of the key challenges facing policymakers, developers, and society as a whole.
Several companies have successfully integrated generative AI into their workflows:
Looking ahead, generative AI is expected to become even more advanced.
We can anticipate:
To use generative AI effectively:
Generative AI is more than just a technological trend — it represents a paradigm shift in how we create and interact with digital content. From boosting productivity to enabling new forms of artistic expression, it offers enormous opportunities. However, with these opportunities come responsibilities. As we navigate this exciting frontier, the challenge will be to harness generative AI in ways that benefit society, respect ethics, and inspire creativity for generations to come.
Section Description